Whereas the cohort study is concerned with frequency of disease in exposed and non-exposed individuals, the case-control study is concerned with the frequency and amount of exposure in subjects with a specific disease (cases) and people without the disease (controls).
- What is case cohort study?
- What is the difference between case control study and cross sectional study?
- Do cohort studies have controls?
- What is case control study in research?
- What is an example of a cohort study?
- How do you identify a cohort study?
- What is an example of a case-control study?
- What are the 3 major types of epidemiologic studies?
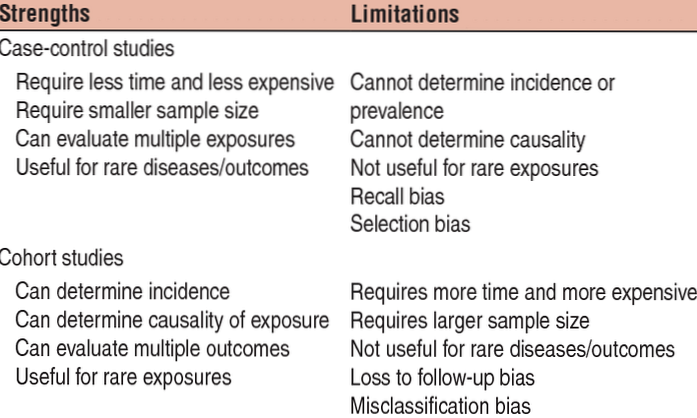
- What are the advantages of case-control studies?
- What are the characteristics of a cohort study?
- Is a case-control study a cohort study?
- What are the advantages of cohort study?
What is case cohort study?
Definition. In a case-cohort study, cases are defined as those participants of the cohort who developed the disease of interest, but controls are identified before the cases develop. ... Case-cohort studies are very similar to nested case-control studies .
What is the difference between case control study and cross sectional study?
Cross sectional studies are used to determine prevalence. They are relatively quick and easy but do not permit distinction between cause and effect. Case controlled studies compare groups retrospectively. They seek to identify possible predictors of outcome and are useful for studying rare diseases or outcomes.
Do cohort studies have controls?
Cohort studies differ from clinical trials in that no intervention, treatment, or exposure is administered to participants in a cohort design; and no control group is defined. ... The study is controlled by including other common characteristics of the cohort in the statistical analysis.
What is case control study in research?
A case-control study is designed to help determine if an exposure is associated with an outcome (i.e., disease or condition of interest). In theory, the case-control study can be described simply. First, identify the cases (a group known to have the outcome) and the controls (a group known to be free of the outcome).
What is an example of a cohort study?
One famous example of a cohort study is the Nurses' Health Study, a large, long-running analysis of women's health, originally set up in 1976 to investigate the potential long term consequences of the use of oral contraceptives.
How do you identify a cohort study?
Study Design
A well-designed cohort study can provide powerful results. In a cohort study, an outcome or disease-free study population is first identified by the exposure or event of interest and followed in time until the disease or outcome of interest occurs (Figure 3A).
What is an example of a case-control study?
For example, in a case-control study of the association between smoking and lung cancer the inclusion of controls being treated for a condition related to smoking (e.g. chronic bronchitis) may result in an underestimate of the strength of the association between exposure (smoking) and outcome.
What are the 3 major types of epidemiologic studies?
Three major types of epidemiologic studies are cohort, case-control, and cross-sectional studies (study designs are discussed in more detail in IOM, 2000). A cohort, or longitudinal, study follows a defined group over time.
What are the advantages of case-control studies?
Advantages: They are efficient for rare diseases or diseases with a long latency period between exposure and disease manifestation. They are less costly and less time-consuming; they are advantageous when exposure data is expensive or hard to obtain.
What are the characteristics of a cohort study?
The characteristic feature of a cohort study is that the investigator identifies subjects at a point in time when they do not have the outcome of interest and compares the incidence of the outcome of interest among groups of exposed and unexposed (or less exposed) subjects.
Is a case-control study a cohort study?
Whereas the cohort study is concerned with frequency of disease in exposed and non-exposed individuals, the case-control study is concerned with the frequency and amount of exposure in subjects with a specific disease (cases) and people without the disease (controls).
What are the advantages of cohort study?
A major advantage of cohort studies in general is the possibility to study multiple exposures and multiple outcomes in one cohort. Even rare exposures can be studied, for the index group can be selected on this exposure.
 Differbetween
Differbetween