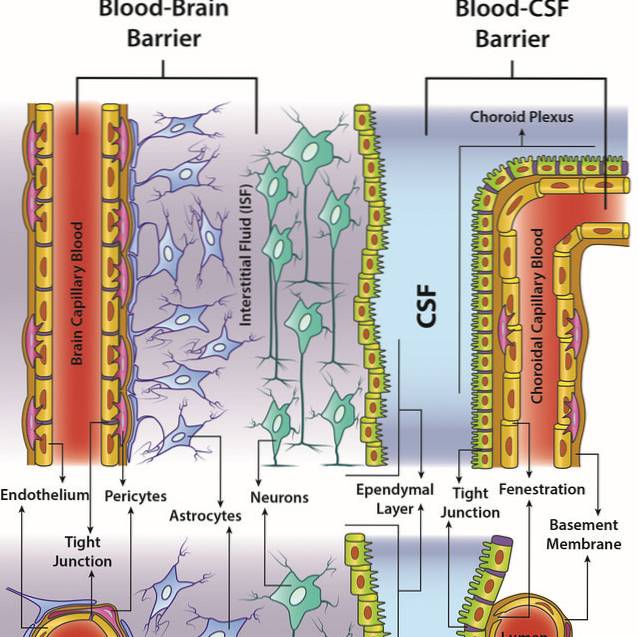
Blood–CSF Barrier Versus Blood–Brain Barrier: Fundamental Differences. ... The parenchymal cells of the BCSFB are the choroid epithelium; on the other hand, BBB is comprised primarily of endothelium. Astrocyte feet covers and modulates most of the BBB, but not the BCSFB.
- What is the blood CSF barrier?
- How can you tell the difference between CSF and blood?
- What is the blood-brain barrier and how does it protect the brain?
- What is the relationship between blood flow and cerebrospinal fluid flow?
- Does CSF cross the blood-brain barrier?
- What passes the blood-brain barrier?
- What is the function of CSF?
- How can an unidentified fluid be determined to be CSF?
- What is the formation of cerebrospinal fluid?
- What Cannot cross the blood brain barrier?
- Does caffeine cross the blood brain barrier?
- What Cannot pass through the blood brain barrier?
What is the blood CSF barrier?
The blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier (BCSFB) is a fluid–brain barrier that is composed of a pair of membranes that separate blood from CSF at the capillary level and CSF from brain tissue. The blood–CSF boundary at the choroid plexus is a membrane composed of epithelial cells and tight junctions that link them.
How can you tell the difference between CSF and blood?
CSF is derived from blood plasma and is largely similar to it, except that CSF is nearly protein-free compared with plasma and has some different electrolyte levels. Due to the way it is produced, CSF has a higher chloride level than plasma, and an equivalent sodium level.
What is the blood-brain barrier and how does it protect the brain?
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a layer of specialized endothelial cells around the brain that protects it—letting in only what is needed and keeping out what could be harmful. It crucially maintains the right ionic balance within the brain and blocks substances that would disrupt essential neural functions.
What is the relationship between blood flow and cerebrospinal fluid flow?
The CSF is produced from components extracted from the blood, so its flow out of the ventricles is tied to the pulse of cardiovascular circulation.
Does CSF cross the blood-brain barrier?
The blood-brain and blood–cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) barriers are able to form an effective barrier to most polar solutes as the expression of tight junctional protein complexes between the endothelial cells of the cerebral vasculature effectively abolish any aqueous paracellular diffusional pathway between blood and ...
What passes the blood-brain barrier?
Only water, certain gases (e.g. oxygen), and lipid-soluble substances can easily diffuse across the barrier (other necessary substances like glucose can be actively transported across the blood-brain barrier with some effort).
What is the function of CSF?
While the primary function of CSF is to cushion the brain within the skull and serve as a shock absorber for the central nervous system, CSF also circulates nutrients and chemicals filtered from the blood and removes waste products from the brain.
How can an unidentified fluid be determined to be CSF?
Diagnosis of a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak:
Diagnosing a CSF leak includes an analysis of the nasal fluid for a protein called beta-2 transferrin which is most only found in cerebrospinal fluid. CT and MRI scans may also be require to determine the location and severity of the leakage.
What is the formation of cerebrospinal fluid?
The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is produced from arterial blood by the choroid plexuses of the lateral and fourth ventricles by a combined process of diffusion, pinocytosis and active transfer. A small amount is also produced by ependymal cells.
What Cannot cross the blood brain barrier?
Furthermore, only a select number of substances can pass through the endothelial cells. Such substances include lipid-soluble substances (e.g., oxygen, carbon dioxide). Hydrophilic substances, for example, hydron and bicarbonate, are not permitted to pass through cells and across the blood-brain barrier.
Does caffeine cross the blood brain barrier?
Caffeine is structurally similar to adenosine, found in our brains. Both molecules are water and fat soluble so they easily cross the blood-brain barrier. In the brain, adenosine protects us by slowing nerve cell activity. Due to its similar structure, caffeine binds to the adenosine receptors.
What Cannot pass through the blood brain barrier?
The blood–brain barrier restricts the passage of pathogens, the diffusion of solutes in the blood, and large or hydrophilic molecules into the cerebrospinal fluid, while allowing the diffusion of hydrophobic molecules (O2, CO2, hormones) and small non-polar molecules.
 Differbetween
Differbetween