- What is normal and anomalous Zeeman effect?
- What is Zeeman effect give the theory of normal Zeeman effect?
- What is Paschen effect?
- What is Stark and Zeeman effect?
- How many types of Zeeman effect are there?
- What is the significance of Lande g factor?
- What is Zeeman effect?
- What causes the Zeeman effect?
- What is JJ coupling and LS coupling?
- What is the difference between Zeeman effect and Stark effect?
- What is linear Stark effect?
- What is ac Stark shift?
What is normal and anomalous Zeeman effect?
The normal Zeeman effect occurs when there is no spin magnetic moment – states with zero spin are necessary. In singulett systems the spins of the electrons cancel each other i.e. add up to zero. ... This is called anomalous Zeeman Effect and can be observed in atomic transitions where non-singulett states are involved.
What is Zeeman effect give the theory of normal Zeeman effect?
Normal Zeeman Effect
For singlet states, the spin is zero and the total angular momentum J is equal to the. orbital angular momentum L. When placed in an external magnetic field, the energy. of the atom changes because of the energy of its magnetic moment in the field, which. is given by.
What is Paschen effect?
: a limiting stage of the Zeeman effect which occurs as the magnetic field causing it is greatly increased and in which the extremely fine structure pattern after going through more or less complicated anomalous stages again approaches a normal triplet character.
What is Stark and Zeeman effect?
The Stark effect is the shifting and splitting of spectral lines of atoms and molecules due to the presence of an external electric field. It is the electric-field analogue of the Zeeman effect, where a spectral line is split into several components due to the presence of the magnetic field.
How many types of Zeeman effect are there?
The spectral lines of mercury vapor lamp at wavelength 546.1 nm, showing anomalous Zeeman effect. (A) Without magnetic field. (B) With magnetic field, spectral lines split as transverse Zeeman effect. (C) With magnetic field, split as longitudinal Zeeman effect.
What is the significance of Lande g factor?
In atomic physics, the Landé g-factor is a multiplicative term appearing in the expression for the energy levels of an atom in a weak magnetic field. The quantum states of electrons in atomic orbitals are normally degenerate in energy, with these degenerate states all sharing the same angular momentum.
What is Zeeman effect?
Zeeman effect,, in physics and astronomy, the splitting of a spectral line into two or more components of slightly different frequency when the light source is placed in a magnetic field.
What causes the Zeeman effect?
The reason for the Zeeman effect is that in a magnetic field, the angular momentum quantum state can undergo a displacement from degeneracy. ... The effect is due to the distortion of the electron orbitals because of the magnetic field. The (normal) Zeeman effect can be understood classically, as Lorentz predicted.
What is JJ coupling and LS coupling?
j-j Coupling
In light atoms, the interactions between the orbital angular momenta of individual electrons is stronger than the spin-orbit coupling between the spin and orbital angular momenta. These cases are described by "L-S coupling".
What is the difference between Zeeman effect and Stark effect?
The main difference between Zeeman effect and Stark effect is that Zeeman effect is observed in the presence of an external magnetic field whereas Stark effect is observed in the presence of an external electrical field.
What is linear Stark effect?
[′lin·ē·ər ′stärk i‚fekt] (atomic physics) A splitting of spectral lines of hydrogenlike atoms placed in an electric field; each energy level of principal quantum number n is split into 2 n - 1 equidistant levels of separation proportional to the field strength.
What is ac Stark shift?
In spectroscopy, the Autler–Townes effect (also known as AC Stark effect), is a type of dynamical Stark effects corresponding to the case when an oscillating electric field (e.g., that of a laser) is tuned in resonance (or close) to the transition frequency of a given spectral line, and resulting in a change of the ...
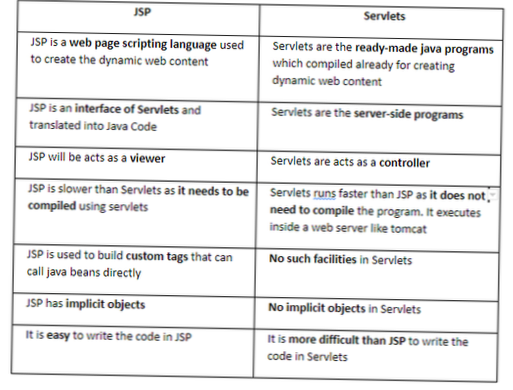
 Differbetween
Differbetween