To determine the equilibrium price, do the following.
- Set quantity demanded equal to quantity supplied:
- Add 50P to both sides of the equation. You get.
- Add 100 to both sides of the equation. You get.
- Divide both sides of the equation by 200. You get P equals $2.00 per box. This is the equilibrium price.
- What is the equilibrium price and quantity?
- What is the equilibrium price and quantity examples?
- How do you calculate QD and Qs?
- How do you find equilibrium price and quantity in Monopoly?
- What increases equilibrium quantity?
- What is the formula for equilibrium price?
- What is the equilibrium quantity?
- What is the difference between market price and equilibrium price?
- What occurs market equilibrium?
- How do you solve market equilibrium?
- What is the formula for calculating demand?
What is the equilibrium price and quantity?
The equilibrium price is the price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. It is determined by the intersection of the demand and supply curves. A surplus exists if the quantity of a good or service supplied exceeds the quantity demanded at the current price; it causes downward pressure on price.
What is the equilibrium price and quantity examples?
When the supply and demand curves intersect, the market is in equilibrium. This is where the quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. ... These two curves will intersect at Price = $6, and Quantity = 20. In this market, the equilibrium price is $6 per unit, and equilibrium quantity is 20 units.
How do you calculate QD and Qs?
P = 10
- P = 10.
- Qd = Qs = 6P = 6(10) = 60 = Q*
- Demand and supply in a market are described by the equations.
- Qd = 120-8P.
- Qs = -6+4P.
- a. Solve algebraically to find equilibrium P and Q.
- P* = 10.5.
- Qd = Qs = 120-8P = 120-8(10.5) = 120-84 = 36 = Q*
How do you find equilibrium price and quantity in Monopoly?
c. If the industry is a monopoly, then the equilibrium price and quantity is found by equating the marginal revenue curve for the monopolist with the marginal cost curve for the monopolist. The MR curve is MR = 1000 – 2Q while the MC curve is the supply curve. Thus, 1000 – 2Q = Q or Q = 333.3.
What increases equilibrium quantity?
An increase in demand and a decrease in supply will cause an increase in equilibrium price, but the effect on equilibrium quantity cannot be detennined. ... If both demand and supply increase, there will be an increase in the equilibrium output, but the effect on price cannot be determined.
What is the formula for equilibrium price?
Given total demand, Q = 3244 - 283P, and domestic demand, Qd = 1700 - 107P, we may subtract and determine export demand, Qe = 1544 - 176P. The initial market equilibrium price is found by setting total demand equal to supply: 3244 - 283P = 1944 + 207P, or P = $2.65.
What is the equilibrium quantity?
Equilibrium quantity is when there is no shortage or surplus of a product in the market. Supply and demand intersect, meaning the amount of an item that consumers want to buy is equal to the amount being supplied by its producers.
What is the difference between market price and equilibrium price?
Market prices are dependent upon the interaction of demand and supply. An equilibrium price is a balance of demand and supply factors. There is a tendency for prices to return to this equilibrium unless some characteristics of demand or supply change.
What occurs market equilibrium?
During market equilibrium; Supply and demand meet at a specific price. At market equilibrium, the supply and demand curves intersect to identify a point where the quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied. The price at this point is the equilibrium price and the quantity obtained is the equilibrium quantity.
How do you solve market equilibrium?
The equilibrium in a market occurs where the quantity supplied in that market is equal to the quantity demanded in that market. Therefore, we can find the equilibrium by setting supply and demand equal and then solving for P.
What is the formula for calculating demand?
In its standard form a linear demand equation is Q = a - bP. That is, quantity demanded is a function of price. The inverse demand equation, or price equation, treats price as a function f of quantity demanded: P = f(Q). To compute the inverse demand equation, simply solve for P from the demand equation.
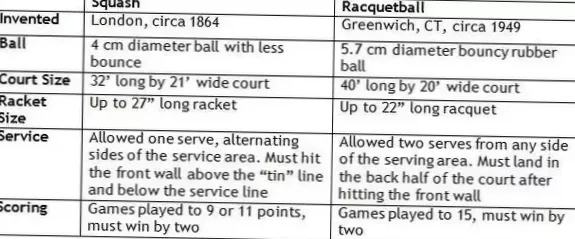
 Differbetween
Differbetween