Roasting involves heating of ore lower than its melting point in the presence of air or oxygen. Calcination involves thermal decomposition of carbonate ores. Roasting is carried out mostly for sulfide minerals. During calcination, moisture is driven out from an ore.
- What is the difference between roasting and calcination give one example for each?
- What is calcination and roasting with example?
- What is calcination and roasting Class 10?
- What is the example of roasting?
- What is the calcination give two examples?
- What do you mean by calcination?
- What is calcination give example?
- Which of the following is an example of calcination process?
- What is calcination explain with reaction?
- Is roasting a reduction process?
- Which ore is used in calcination?
- What is flux and slag?
What is the difference between roasting and calcination give one example for each?
eg: carbon, sulphur etc removed as their gaseous oxides.
...
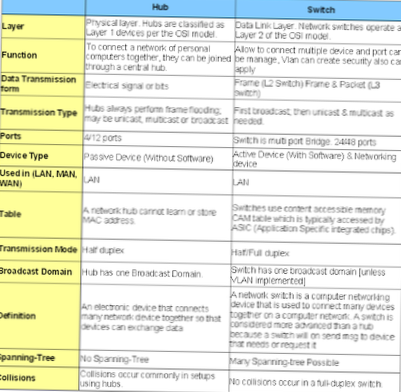
Difference between Roasting and Calcination.
| Roasting | Calcination |
|---|---|
| Example: For the ores ZnS (sphalerite) and Cu2S (chalcocite), balanced equations for the roasting are: 2ZnS+3O2-->2 Zno+ 2SO2 2 Cu2S + 3O2 → 2 Cu2O + 2 SO2 | Example: ZnCO3--> ZnO+ C02 |
What is calcination and roasting with example?
Roasting is a process of heating the concentrated ore to a high temperature in presence of air. Generally, sulfide ores are roasted. Example: 2 ZnS + 3 O2 → 2 ZnO + 2 SO2. Calcination is a process of heating ore in the absence of air to a high temperature but insufficient to melt the ore.
What is calcination and roasting Class 10?
Calcination is the process of heating the ore below its melting point in absence of air to remove volatile impurities like arsenic etc. Roasting is the process in which the ore is heated below its melting point in presence of air to oxidise the impurities.
What is the example of roasting?
Roasting Definition: Roasting is a process in metallurgy in which a sulfide ore is heated in air. The process may convert a metal sulfide to a metal oxide or to a free metal. Example: Roasting ZnS may yield ZnO; roasting HgS may yield free Hg metal.
What is the calcination give two examples?
A typical calcination process involves the conversion of calcium carbonate to calcium oxide. Some other common examples of calcination include; Calcination of limestone involving decomposition of carbonate ores and removal of carbon dioxide. ... Decomposition of volatile components from raw petroleum coke.
What do you mean by calcination?
Calcination, the heating of solids to a high temperature for the purpose of removing volatile substances, oxidizing a portion of mass, or rendering them friable. Calcination, therefore, is sometimes considered a process of purification. Calcination. Heat-treating. Roasting.
What is calcination give example?
Calcination is the process of heating the concentrated ore such as carbonate or hydrated oxide to a high temperature in the absence of air. Example: Metal carbonates get decomposed to produce metal oxides. Z n C O X 3 ⟶ Z n O + C O X 2.
Which of the following is an example of calcination process?
The process of conversion of a concentrated on into its oxide by heating in absence or in limited supply of air is called calcination. It is usually done for hydroxide and carbonate ores. Thus, MgCO3Δ→MgO+CO2 is an example of calcination process.
What is calcination explain with reaction?
Calcination: It is a process in which the ore is heated to a high temperature below the melting point of metal in absence of air or limited supply of air. The change that takes place during calcination with reactions are: ∙ Moisture and water from hydrated ores, volatile impurities and organic matter are removed.
Is roasting a reduction process?
Roasting consists of thermal gas–solid reactions, which can include oxidation, reduction, chlorination, sulfation, and pyrohydrolysis. In roasting, the ore or ore concentrate is treated with very hot air. This process is generally applied to sulfide minerals.
Which ore is used in calcination?
Calcination involves the thermal decomposition of carbonate ores.
What is flux and slag?
1)Flux is the material or substance thats is added to molten metals to bond with impurities that can be readily removed whereas slag is the waste material which is removed. Fluxes are used during the refining of metals.
 Differbetween
Differbetween