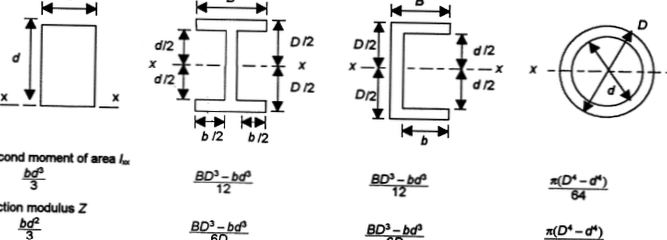
Moment of inertia is the sum of the products of the mass of each particle in the body with the square of its distance from the axis of rotation. Modulus of cross-section or section modulus is a geometric property for a given cross-section used in the design of beams or flexural members.
- What is the difference between moment of inertia and modulus of elasticity?
- What is the difference between elastic and plastic section modulus?
- How do you calculate plastic modulus?
- What is the relation between sectional modulus and moment of inertia for any standard section?
- What is plastic moment resistance?
- What section modulus tells us?
- What is a slender section?
- What is polar section modulus?
- What is elastic moment capacity?
- What is bending stress formula?
- What is Z in moment of inertia?
- What is Z in bending stress?
What is the difference between moment of inertia and modulus of elasticity?
MODULUS OF ELASTICITY: The ratio of stress to strain or the stiffness of the material of a structural member (resistance to deformation). ... MOMENT OF INERTIA: The bending stiffness of a structural member's cross-sectional shape. Moment of inertia is specific to bending of the cross section of the member .
What is the difference between elastic and plastic section modulus?
What's the difference between plastic section modulus and elastic section modulus? ... The elastic section modulus assumes the section remains elastic. The plastic section modulus assumes the entire section yields. Elastic modulus is the steel modulus based on the stress strain curve before yielding.
How do you calculate plastic modulus?
The plastic section modulus for a rectangular cross section can be determined by multiplying each section half (e.g., the shaded area shown in Figure 1.50) by the distance from its centroid to the centroid for the whole section: Zx = B(H/2)(H/4) + B(H/2)(H/4) = BH2/4.
What is the relation between sectional modulus and moment of inertia for any standard section?
The elastic section modulus is defined as S = I / y, where I is the second moment of area (or area moment of inertia, not to be confused with moment of inertia) and y is the distance from the neutral axis to any given fibre.
What is plastic moment resistance?
It is defined as the moment at which the entire cross section has reached its yield stress. This is theoretically the maximum bending moment that the section can resist - when this point is reached a plastic hinge is formed and any load beyond this point will result in theoretically infinite plastic deformation.
What section modulus tells us?
Section modulus is a geometric property for a given cross-section used in the design of flexural members. ... The bending moment that it takes to yield that section equals the section modulus times the yield strength. In simple terms, the section modulus is the ratio of bending moment to bending stress for steel.
What is a slender section?
Explanation: Slender or class IV sections are cross section in which local buckling occurs even before the yield stress is attained in one or more parts of the cross section.
What is polar section modulus?
Polar modulus is defined as the ratio of the polar moment of inertia to the radius of the shaft. It is also called as torsional section modulus.
What is elastic moment capacity?
Elastic moment strength is the maximum moment that a member can withstand before plastic deformation due to yielding. Due to yielding, cross sectional plane will no longer retains the same shape before and after bending. The elastic moment strength is used to determine the yield strength of member due to bending.
What is bending stress formula?
The bending stress (σ) is defined by Eq. (1.5). M is the bending moment, which is calculated by multiplying a force by the distance between that point of interest and the force. c is the distance from the NA (in Fig. 1.5) and I is the moment of inertia.
What is Z in moment of inertia?
The moment of inertia (MI) of a plane area about an axis normal to the plane is equal to the sum of the moments of inertia about any two mutually perpendicular axes lying in the plane and passing through the given axis. • That means the Moment of Inertia I. z. = I. x.
What is Z in bending stress?
R=radius of curvature. From the bending equation M/I = σ/y. Or, M = σI/y = σ Z, where Z is the section modulus. The line of intersection of the neutral layer with any normal cross section of a beam is known as neutral axis of that section. BEAMS OF UNIFORM STRENGTH.
 Differbetween
Differbetween