The key difference between glycosylation and glycosidation is that glycosylation is the process that attaches a carbohydrate to a protein or a lipid molecule while glycosidation is the process of forming a glycoside. ... Both glycosylation and glycosidation involve sugar or carbohydrates.
- What is the meaning of Glycosidation?
- What is Lipid Glycosidation?
- What does glycosylation do to a protein?
- What is glycosylation in Golgi complex?
- What is the purpose of glycosylation?
- How many proteins are glycosylated?
- How is protein glycosylation detected?
- Does glycosylation affect protein folding?
- Is glycosylation reversible?
- Where does glycosylation start?
- Are glycosylated proteins more flexible?
- Where does glycosylation happen?
What is the meaning of Glycosidation?
Fischer glycosidation (or Fischer glycosylation) refers to the formation of a glycoside by the reaction of an aldose or ketose with an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst. ... Commonly, the reaction is performed using a solution or suspension of the carbohydrate in the alcohol as the solvent.
What is Lipid Glycosidation?
Glycosylation is the process by which a carbohydrate is covalently attached to a target macromolecule, typically proteins and lipids. This modification serves various functions. For instance, some proteins do not fold correctly unless they are glycosylated.
What does glycosylation do to a protein?
Glycosylation, the attachment of sugar moieties to proteins, is a post-translational modification (PTM) that provides greater proteomic diversity than other PTMs.
What is glycosylation in Golgi complex?
Glycosylation is a very common modification of protein and lipid, and most glycosylation reactions occur in the Golgi. ... The spectrum of glycosyltransferases and other activities that effect glycosylation may vary with cell type, and thus the final complement of glycans on glycoconjugates is variable.
What is the purpose of glycosylation?
Glycosylation is an important and highly regulated mechanism of secondary protein processing within cells. It plays a critical role in determining protein structure, function and stability. Structurally, glycosylation is known to affect the three dimensional configuration of proteins.
How many proteins are glycosylated?
A total of 534 proteins were identified, 406 of which were previously not known to be glycosylated. Many proteins in the secretory pathway were identified, as well as other functional classes of proteins, including TFs and mitochondrial proteins.
How is protein glycosylation detected?
Glycan Structure Analysis. After protein glycosylation has been confirmed, the glycan moiety structure can be elucidated by chromatography and mass spectrometry. The glycan could be analyzed when attached to the protein or following its release.
Does glycosylation affect protein folding?
Glycosylation starts at the endoplasmic reticulum during protein synthesis in the ribosome. ... Although glycans can assist protein folding, their removal from folded proteins often does not affect the protein fold and function.
Is glycosylation reversible?
Although glycation is a reversible reaction, it is considered a first step in the Maillard or browning reaction, which leads to irreversible chemical modification, browning, generation of fluorescence, and cross-linking of proteins during cooking.
Where does glycosylation start?
N-linked glycosylation actually begins in the endoplasmic reticulum, but O-linked glycosylation does not occur until the polypeptide has been transported into the Golgi apparatus.
Are glycosylated proteins more flexible?
Previous studies on the effects of glycosylation on protein folding and stability have found that the primary effect of glycosylation is to destabilize the denatured state[26]. ... Regarding native state dynamics, glycosylation increases flexibility in some regions and decreases it in others (Figure 6).
Where does glycosylation happen?
Protein glycosylation is an enzyme-directed chemical reaction that takes place in the ER(Endoplasmic Reticulum) and in the Golgi Apparatus body of the cell. General glycosylation within the ER helps with folding, and glycosylation in the Golgi body tells a protein where to go.
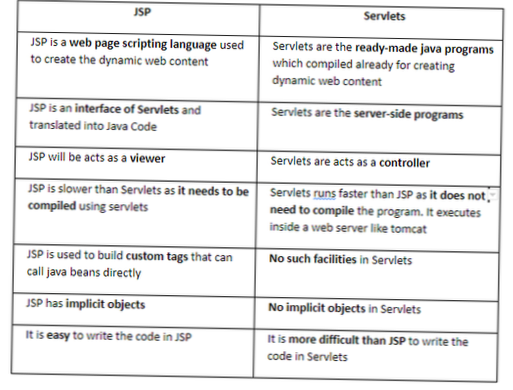
 Differbetween
Differbetween